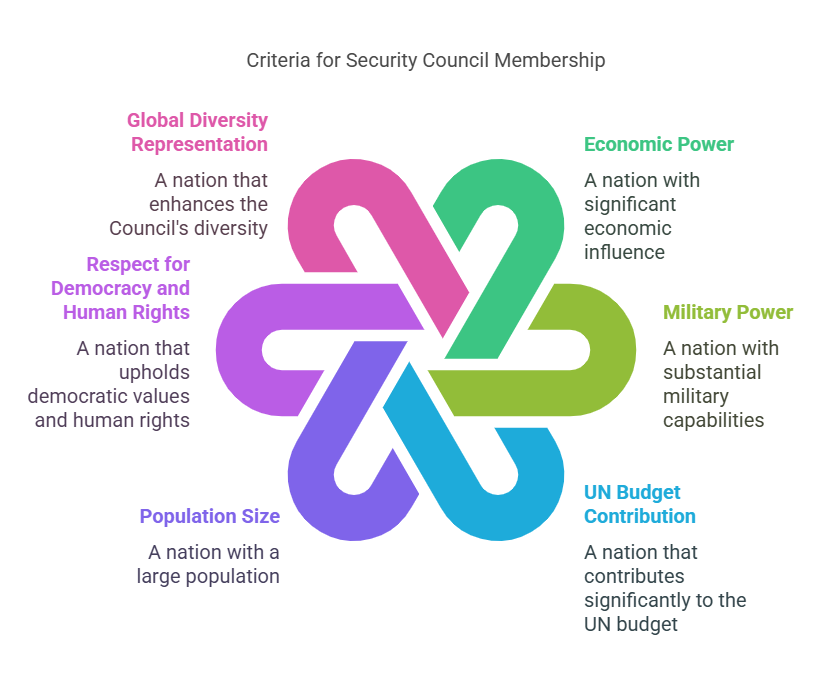
Criteria for new member?
International organizations are formal institutions with membership from multiple countries that work on issues of common interest. They play crucial roles in maintaining peace, promoting cooperation, and addressing global challenges.
| Organ | Composition | Functions |
|---|---|---|
| General Assembly | All member states (1 vote each) | Deliberative policymaking body |
| Security Council | 15 members (5 permanent) | Maintain peace and security |
| Economic and Social Council | 54 members | Coordinates economic/social work |
| International Court of Justice | 15 judges | Judicial organ |
| Secretariat | Secretary-General + staff | Administrative functions |

Criteria for new member?
| Organization | Established | Members | Purpose |
|---|---|---|---|
| European Union (EU) | 1993 | 27 countries | Economic and political integration |
| ASEAN | 1967 | 10 SE Asian nations | Regional cooperation |
| SAARC | 1985 | 8 South Asian nations | Regional development |
| African Union (AU) | 2002 | 55 African nations | Political and economic integration |