🏭 Introduction
Secondary activities are concerned with the processing of natural resources into usable products. These include all types of manufacturing industries and construction work.
🏗️ Characteristics of Secondary Activities
- Use of raw materials from primary sector.
- Involves skilled labor and machinery.
- Converts raw material into valuable goods.
- Usually located near markets or resources.
- large capital
- large number of employees
🏢 Types of Manufacturing Industries
- Agro-based: Sugar, Cotton, Tea industries.
- Mineral-based: Iron and Steel, Cement, Aluminum.
- Forest-based: Paper, Furniture.
- Chemical-based: Petrochemical, Fertilizer, Paint.
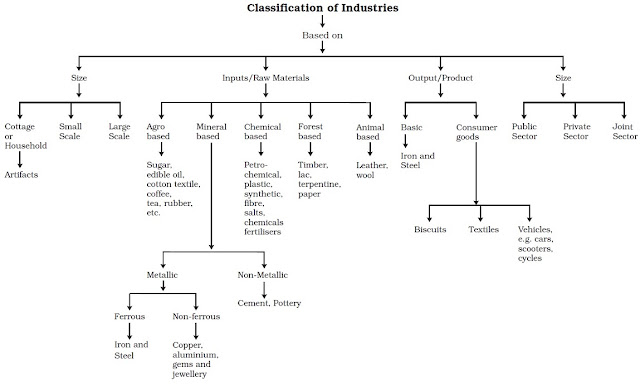
🌐 Classification of Industries
- Size: Cottage, Small-scale, Large-scale industries.
- Ownership: Public sector, Private sector, Joint sector, Cooperative sector.
- Based on Raw Material: Agro-based, mineral-based, forest-based, marine-based.
- Based on Output: Basic (e.g., iron & steel) and consumer goods industries.
🧠 Mind Map – Secondary Activities
🪙 Footloose Industries
These are industries that are not tied to any specific raw material or market location. They can be set up anywhere and include electronics, software, and light manufacturing industries.
🏙️ Industrial Regions (Factors affecting their location)
Industrial regions are areas with high concentration of industries. Factors affecting their location include:
- Availability of raw materials
- Power supply
- Skilled labor
- Market access
- Transport and communication
- Capital and infrastructure
- Government policies
🌍 Impact of Industrialization
- Positive: Economic growth, employment, urbanization
- Negative: Pollution, environmental degradation, regional imbalance
📖 Conclusion
Secondary activities transform raw materials into finished goods, supporting economic development. Their efficient management is vital for sustainable growth.