🌍 Introduction
The study of world population includes the understanding of where people live, how densely populated regions are, and how population grows or declines over time. These patterns are influenced by environmental, social, political, and economic factors.
📌 Population Distribution
Population distribution refers to the pattern of where people live across the earth. It is uneven due to various natural and human-made factors.
I. Geographical Factors
(i) Availability of Water
Water is the most important factor for life, which is why people prefer to live in areas where fresh water is easily accessible. Additionally, water bodies facilitate navigation.
(ii) Landforms
People tend to settle on flat plains and gentle slopes because these areas are favorable for agriculture, road construction, and industrial development. In contrast, mountainous and hilly regions
(iii) Climate
Extreme climates, such as hot or cold deserts, are uncomfortable for human habitation. Regions with moderate climates and minimal seasonal variations attract more settlements
(iv) Soils
Fertile soils support intensive agriculture and allied activities, making areas with loamy soils more densely populated
II. Economic Factors
(i) Minerals
Areas rich in mineral resources attract mining and industrial activities, creating job opportunities. This draws skilled and semi-skilled workers, leading to higher population density. An example is the Katanga-Zambia copper belt in Africa.
(ii) Urbanisation
Cities provide better employment, education, healthcare, transport, and communication facilities leads to rural-to-urban migration
(iii) Industrialisation
Industrial regions offer numerous job opportunities, attracting not only factory workers but also professionals. The Kobe-Osaka region in Japan is a prime example
III. Social and Cultural Factors
Places with religious or cultural significance often attract more people, while regions with social or political unrest see outmigration.
📊 Population Density
Population density is the number of people living per unit area, usually per square kilometer.
Population Density = Total Population/Total Land Area
- High Density: Bangladesh, India, Japan
- Low Density: Australia, Canada, Mongolia
📈 Population Growth
Population growth is the increase in the number of individuals in a population. It occurs in two major ways:
(Components ofpopulation change )
- Natural Growth: Birth rate minus death rate
(Actual growth:Birth-death+ migration in - migration out)
- Migration: Movement of people from one place to another(Push factor and pull factor)
The crude birth rate (CBR)
is expressed as number of live births in a year per thousand ofpopulation
Crude death rate(CDR) is expressed as number of deaths in a particular year perthousand of population in a particular region
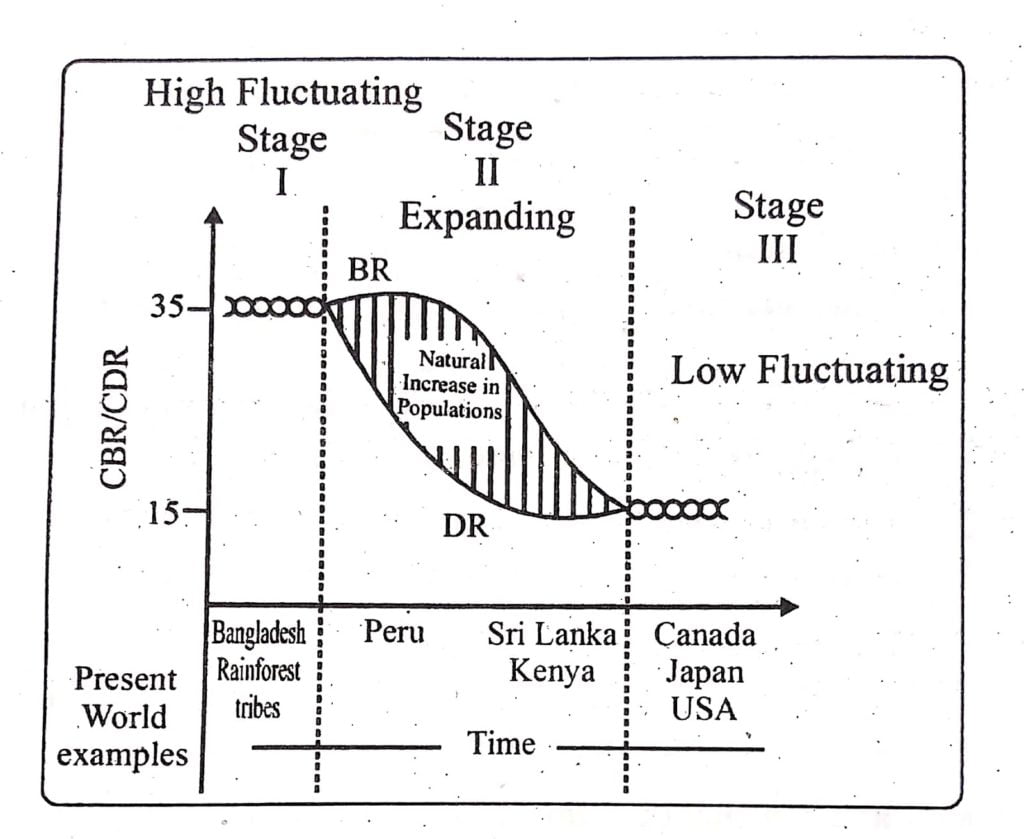
🧮 Demographic Transition
The theory states that as a society develops—transitioning from a rural, agrarian, and illiterate structure to an urban, industrial, and educated one—its population dynamics shift from high birth and death rates to low birth and death rates
Demographic transition is a model that describes population change over time through three stages:
- High fluctuating stage: High birth and High death rates.ex- Bangladesh
- Expanding stage : (A)High birth rate and declining death rate. ex-Peru
(B) Declining birth and death rates. ex- Sri lanka
Low fluctuating or Declining stage : Low birth and death rates Ex- Canada,Japan
📖 Conclusion
Understanding population distribution and growth helps in planning for resources, infrastructure, and sustainable development. It is a crucial element in both human and economic geography.
